Data Governance Strategy: A Must Have for Every Organizations
In this tech-driven era, data is at the center, ensuring success in an increasingly competitive and discerning market. It’s the lifeblood that fuels informed decisions, innovation, and meeting the ever-evolving demands of a tech-savvy customer base.

“Analysts estimate that 80% of organizations seeking to scale digital business will fail by 2025 because they do not take a modern approach to data governance. All organizations need to plan how they use data so that it is handled consistently throughout the business to support business outcomes.”- Gartner
What is Data Governance?
Organizations rely on data governance, a comprehensive system of rules and procedures, to ensure their data is of high quality, secure, accessible, and useful. It encompasses processes, roles, responsibilities, and technologies designed to oversee and protect data throughout its entire lifecycle. Think of data governance as the compass that steers an organization’s data journey, comprising strategies, policies, and the people responsible for data management. At its core, data governance serves two crucial purposes: first, ensuring data adheres to both external regulations and internal standards, and second, safeguarding data against security breaches. Additionally, it establishes clear ownership and accountability for data assets. This not only upholds data integrity but also optimizes data organization and utilization, delivering tangible benefits like informed decision-making and overall success for the organization.
Why Have a Strong Data Governance Strategy?
Organizations routinely store unstructured data from diverse sources in non-relational databases or data lakes, creating a challenge in understanding and managing this data effectively. The initial step in implementing data governance strategy involves establishing data capture processes tailored to the specific needs of your business and its various departments, avoiding the collection of excessive, unnecessary data. Data governance serves as a cornerstone for maximizing the value derived from data assets, while also acting as a shield against potential risks like data breaches and compliance violations. Furthermore, it plays a pivotal role in cultivating trust among stakeholders, including customers, partners, and regulatory bodies.
Creating a strong data governance strategy is valuable, to make it work for your organization’s specific goals. While each company’s plan will be different, there are some important principles to keep in mind when building and using data governance. Key objectives include:
- Proper Data Use: Make sure data is used correctly, reducing errors and misuse. Clear data use rules and effective monitoring processes are key, including technical and business details.
- Enhanced Data Security: Keep all data secure and prevent unauthorized access.
Issues with unclear reports often lead to technology being unjustly blamed. In many cases, the root cause lies in misconfigured tools and systems or their inappropriate applications, such as using reporting tools on production databases, which can hamper both transactional and analytical processes. Rather than resorting to replacing fundamentally sound systems, a more cost-effective and efficient approach lies in the improvement of data governance practices. By clearly specifying how an organization collects, stores, backs up, and safeguards its data against accidents, theft, or misuse, effective data governance serves as a shield against such issues, ensuring data reliability and security.
Further Read: Why Businesses Need a Powerful Data Strategy? 6 Ultimate Reasons
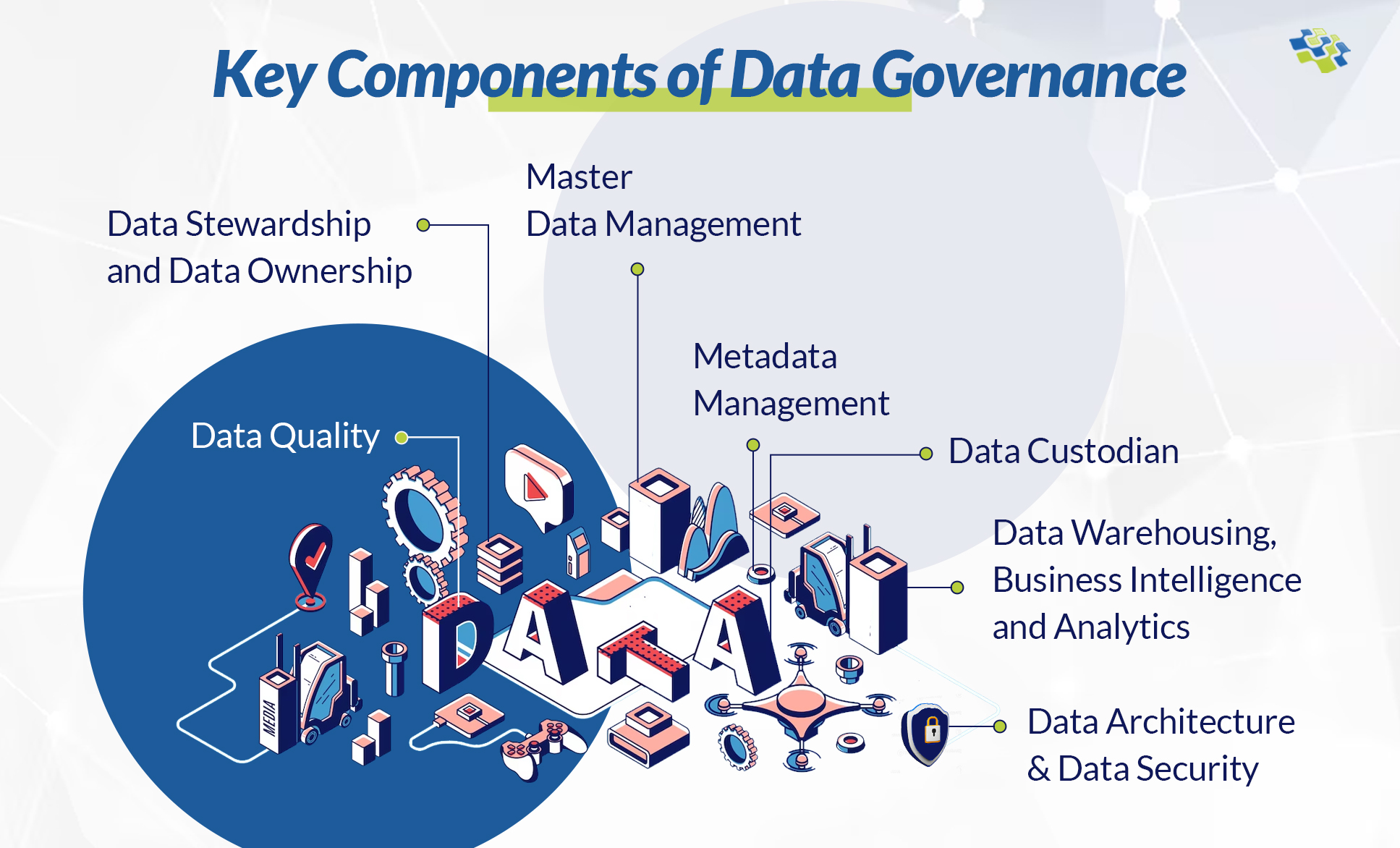
Data Governance Key Components
A data governance strategy involves essential elements critical for success in managing data effectively and ensuring compliance.
 1. Data Quality
1. Data Quality
In a data governance strategy, the primary goal is to improve data quality. Imagine data governance as the guardian of data quality within a company. It’s crucial role is to ensure that the data utilized by the organization is accurate, complete, current, and complaint with established standards and business regulations. It achieves this by overseeing the entire data lifecycle, from its initial collection through storage, processing, and management. There are six fundamental facets of data quality standards addressed by data governance: completeness, comprehensibility, consistency, accuracy, availability, and integrity. By actively managing these aspects, data governance ensures that the data used by the organization is not only trustworthy but also supports effective decision-making, promoting efficiency and reliability across the entire data ecosystem.
2. Data Stewardship & Data Ownership
The data governance process determines who is responsible for managing data. It designates data ownership and stewardship roles, specifying who does what. Good data governance strategy not only clarifies these roles but also explains how they work together in detail, ensuring smooth data management.
- The Data Governance Council: They hold the power to create crucial program policies and greenlight the methods for putting those policies into action. These individuals are seasoned senior team members well-versed in the organization’s operations and long-term strategy.
- Data Stewards: Subject-matter experts are the ones who turn the policies set by the data governance council into reality. They are responsible for maintaining high data quality and maximizing its value within the organization.
- Data Producers or Consumers: These are the individuals who create data using applications or rely on data to make decisions in various business processes. They have the crucial role of executing the data governance plan and ensuring that data is handled correctly according to established rules and guidelines.
- Data Owners: These are the leaders responsible for ensuring that data within a specific area is properly managed across different systems and business units. They offer insights to the council and stay informed about the program’s progress through regular updates.
3. Metadata Management
Data about data is metadata, often referred to as the unsung hero of data analytics. Meta data is the information that provides context about specific data, such as its format, source, creation date, versioning etc. This metadata is like a data’s lineage, giving it a history and identity. It plays a pivotal role in data management because it helps us understand the data’s quality, relevance, and reliability, instilling confidence in its use. In today’s intricate data systems, keeping tabs on metadata can be a formidable task. However, it’s an indispensable aspect of effective data governance strategy. Metadata holds the essential details needed to transform diverse datasets into coherent models for analysis. It encapsulates information ranging from the conceptual understanding of data to its logical and physical attributes. For organizations serious about data management, incorporating a metadata management strategy within their data governance framework is paramount. It ensures that data remains comprehensible, trustworthy, and valuable, facilitating informed decision-making and enhancing the overall data analytics process.
4. Master Data Management
Master Data Management (MDM) is a critical component of a data governance strategy. It focuses on identifying and managing core data elements that are shared across an organization, such as customer information, product data, or employee details. It ensures that these core data elements are consistent, accurate, and up to date across all systems and departments. A study found that “poor data quality costs organizations an average of $15 million per year in losses.” This underscores the importance of MDM in data governance. When MDM is implemented effectively, it reduces data errors, minimizes duplication, and enhances data reliability. Think of MDM as the custodian of your most important data, making sure it’s clean, consistent, and trustworthy. This not only boosts operational efficiency but also helps organizations make better-informed decisions based on reliable data, leading to improved business performance.
5. Data Custodian
As the custodian of a company’s sensitive data, the data custodian acts as a guardian for the data’s value. This role carries the responsibility of ensuring the high quality of these data assets. They act as a mediator in resolving disputes that arise during user group meetings, using their expertise to find solutions. If a dispute involves stakeholders from different divisions and becomes politically sensitive, it’s the data custodian’s job to elevate it to the Data Governance (DG) Council for resolution. In addition to quality assurance and dispute resolution, data custodians play a pivotal role in approving plans related to data management, data cleansing, and ensuring data is suitable for its intended purposes. They bridge the gap between strategic plans and practical implementation, manage changes in data processes, and handle stakeholder relationships.
6. Data Warehousing, Business Intelligence & Analytics
Data warehousing, business intelligence (BI), and analytics have evolved into distinct solutions within many organizations. Effective data governance plays a pivotal role in optimizing the processing of analytical data and streamlining the acquisition of decision-support data for reporting and analysis. Furthermore, data governance fosters a culture of collaboration across the entire enterprise, encouraging innovative uses of analytics by establishing a shared understanding of data. Data governance acts as the backbone for efficient data management, facilitating better decision-making through reliable, well-organized data, and promoting a culture of data-driven innovation within organizations.
Read Our Success Story to Learn About
7. Data Architecture & Data Security
Data architecture and Data security are fundamental pillars of a robust data governance strategy. Data architecture involves designing how data is stored, organized, and accessed within an organization. It’s like planning the blueprint of a building. A well-thought-out data architecture ensures data is structured efficiently and can be easily retrieved when needed, promoting data quality and usability. Data security, on the other hand, is like the lock and key to that building. It involves safeguarding data from unauthorized access, breaches, and cyber threats. Data breaches can be incredibly costly, with an average global cost of $3.86 million per breach. Together, Data architecture and Data security form the backbone of data governance. They ensure data is both accessible and protected. When these components are effectively managed, organizations can trust their data, make informed decisions, and minimize the risk of costly security breaches.
How NextGen Invent Used Data Governance Framework?
NextGen Invent has effectively employed a data governance framework to enhance its data management practices. We have established key governance bodies, namely the Business Community Council and the Technology Community Council. The Business Community Council plays a pivotal role in setting policies, managing business demands, making informed investment decisions, and ensuring ongoing funding availability for data-related initiatives. This council also identifies opportunities and challenges, evaluates costs and benefits, defines priorities, and diligently monitors progress. Simultaneously, the Technology Community Council focuses on confirming technical architecture direction, managing technology-related demands, and maintaining consistency through the enforcement of patterns and tools within the Enterprise Data Warehouse Environment (EDWE).
In addition to these governance bodies, we maintained a Program Office with specific responsibilities, including data quality oversight, metadata management, resolution of data-related issues, establishment of performance and quality metrics, maintenance of business rules, and ensuring the availability of necessary processes and infrastructure for smooth data operations. By implementing this comprehensive data governance framework, we at NextGen Invent ensured data accuracy, accessibility, and security while effectively aligning business and technology strategies to optimize data management practices.
Further Read: 6 Data Management Best Practices to Improve Data Performance
Conclusion
A well-structured enterprise data governance strategy is not just a choice but a necessity for every organization in today’s data-driven landscape. It’s the blueprint that ensures data is managed efficiently, securely, and in a way that adds value to your operations. Without a robust data governance strategy, the risks of data mishandling, breaches, and missed opportunities loom large. To thrive in the era of data, organizations must embrace data governance as a fundamental pillar of their success. At NextGen Invent, we specialize in empowering businesses with cutting-edge data strategy governance and analytics solutions.
Contact us today for a consultation and discover how we can drive your organization’s success through data-driven insights and innovation.
Stay In the Know
Get Latest updates and industry insights every month.
 1. Data Quality
1. Data Quality