Which Blockchain framework will fit your business needs?
With the rapid advancement of technology, there are now numerous blockchain framework available for use. It is natural to wonder about the differences between these platforms and the specific capabilities of each. Some of the most well-known and prominent blockchains include Bitcoin, Ethereum, Ripple, Hyperledger, LISK, and Stellar.
These blockchain frameworks have gained significant attention as they continue to improve and secure their chains and have developed a range of capabilities to meet the diverse needs of users. It can be challenging to choose the right blockchain platform for a specific project but understanding the unique features and capabilities of each can help make the decision-making process easier.

Bitcoin
Bitcoin is a widely recognized blockchain platform that is primarily used for its cryptocurrency, known as bitcoin or BTC. It was the first practical application of blockchain technology and has gained significant media attention. Transactions on the Bitcoin network are recorded on a distributed ledger, and the network relies on a complex mining process to validate these transactions and add them to the blockchain. This process involves using specialized computers to solve complex mathematical problems, which requires a significant amount of computational power.
| Pros | Cons | Use Cases |
|---|---|---|
|
|
|
Ethereum
Ethereum is a popular blockchain platform that is often compared to Bitcoin. Like Bitcoin, Ethereum has its own cryptocurrency called Ether (ETH). In addition to being a platform for digital currency transactions, Ethereum also supports the development of decentralized applications (dApps). The Ethereum wallet also has support for ERC-20 tokens, which are a form of digital asset that are associated with specific applications or projects on the Ethereum blockchain.
| Pros | Cons | Use Cases |
|---|---|---|
|
|
|
Ripple
Ripple is a blockchain platform that was designed to enable fast and low-cost transactions between large organizations. It has its own native cryptocurrency called XRP, which is used to facilitate these transactions. Ripple is known for its ability to handle high volumes of transactions and its focus on catering to the needs of large enterprises.
| Pros | Cons | Use Cases |
|---|---|---|
|
|
|
Hyperledger
Hyperledger is an open source blockchain platform that offers smart contract functionality similar to Ethereum. It is geared towards large-scale businesses and their associated transactions. Unlike many other blockchain platforms, Hyperledger does not have its own native cryptocurrency. Instead, it is focused on providing a secure and scalable platform for enterprise use cases.
| Pros | Cons | Use Cases |
|---|---|---|
|
|
|
Lisk
Lisk is a blockchain platform that is designed to support the development of decentralized applications (dApps) using JavaScript. It promotes the creation of dApps and even maintains a directory of available dApps for users to browse and discover. Lisk has its own cryptocurrency called LSK, which is used to facilitate transactions on the platform. Lisk is known for its focus on developer accessibility and its use of JavaScript, which is a widely used programming language.
| Pros | Cons | Use Cases |
|---|---|---|
|
|
|
Stellar
Stellar is a blockchain platform that supports simple smart contracts. It is not as well-suited for the development of decentralized applications (dApps) as some other platforms due to its non-Turing complete computing environment, which means it lacks the full range of computational capabilities found on platforms like Ethereum. Despite this limitation, Stellar has gained widespread adoption due to its focus on enabling fast and low-cost transactions and its support for a variety of use cases, including cross-border payments and microfinance. It has its own native cryptocurrency called Lumens (XLM), which is used to facilitate transactions on the platform.
| Pros | Cons | Use Cases |
|---|---|---|
|
|
|
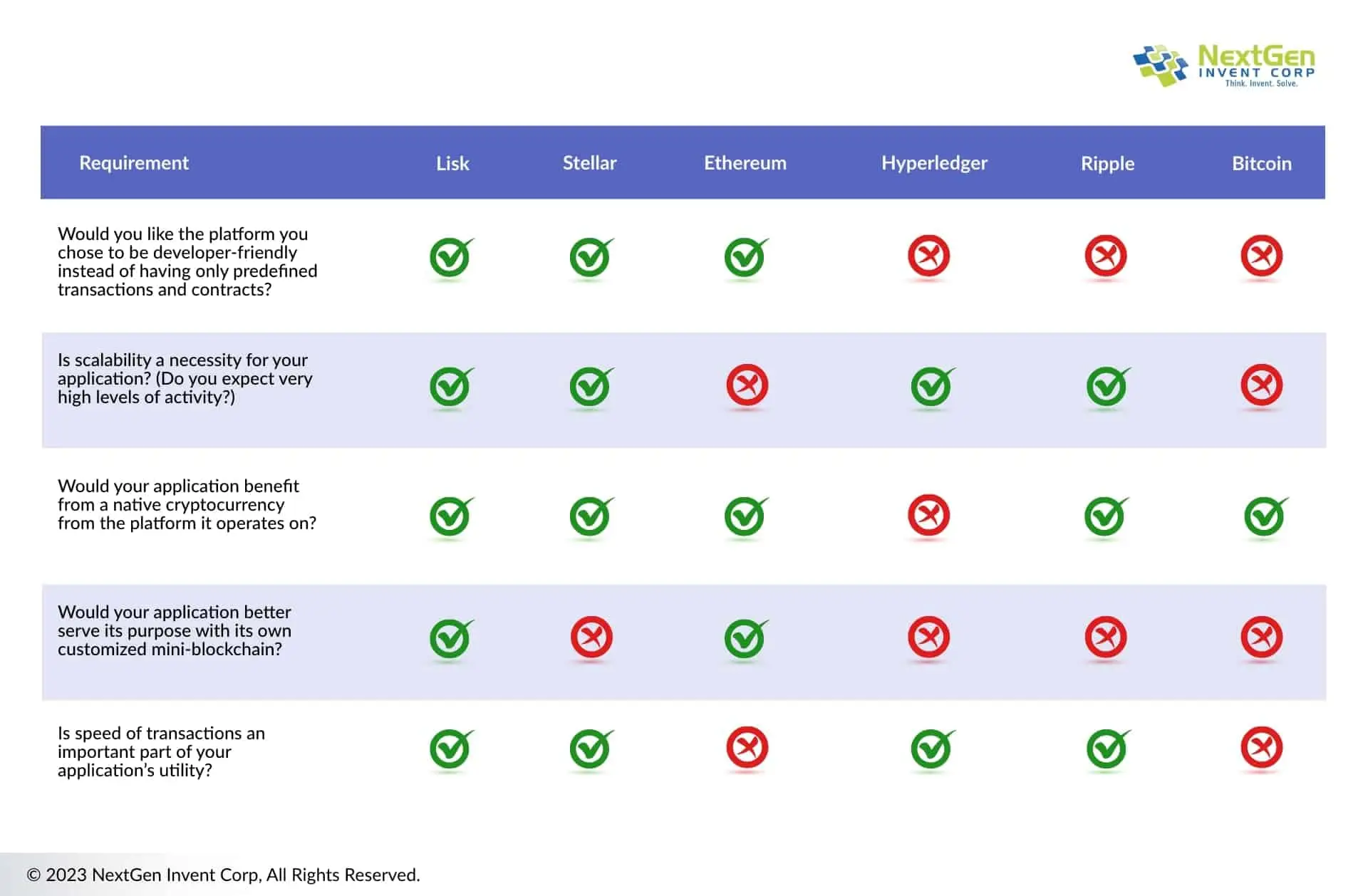
Which blockchain framework is best for which use cases?
 Conclusion
Conclusion
When choosing a blockchain framework, it is important to consider the specific requirements and goals of your business, as well as the unique features and capabilities of each platform. Some platforms may be better suited for certain use cases, such as Ethereum for dApp development or Hyperledger for enterprise applications. Others may be more focused on specific features, such as Ripple’s emphasis on low-cost, high-volume transactions or Lisk’s support for JavaScript development. By carefully evaluating your needs and comparing the different options available, you can determine the blockchain framework that best fits your business needs.
Stay In the Know
Get Latest updates and industry insights every month.
 Conclusion
Conclusion