Remote Patient Monitoring Services: Top Benefits, Features, and Key Steps for Development
We’ll go over how these technologies can be used to improve patient happiness, cut down on needless hospital stays, and expedite healthcare services. We’ll also go over remote patient monitoring software development steps, benefits, and features.

Concerned About Patient Engagement? Our Custom AI mHealth App Development Services Deliver Intuitive, Patient-Centric Experiences

“The remote patient monitoring market’s growth is driven by the healthcare-related cost advantage owing to the adoption of RPM. Additionally, there is a growing emphasis on patient-centered care, and RPM empowers patients to actively participate in their health management. This aligns with the trend towards personalized medicine and patient engagement driving the RPM market during the forecast period.”- Markets And Markets
What is Remote Patient Monitoring: Overview
Let’s think about a patient monitoring system before getting into the precise definition of remote patient monitoring. This includes any tools and procedures used by medical professionals to keep an eye on critical biological markers. Electrocardiography equipment, for instance, is a typical tool in a patient monitoring system that enables doctors to keep an eye on the vital signals of the heart.
An RPM system is more than just a piece of technology used to track patients’ vital signs. It uses the IoT and the most recent developments in information technology to collect patient data outside of clinics and hospitals. RPM can be broadly classified into two types according to their application: remote (at home) and bedside (at a hospital or doctor’s office). Various kinds of systems fall under these categories:
- Cardiac Monitoring: Real-time remote patient status monitoring is accomplished via low-amplitude signals. It is intended especially for patients who have implanted heart monitors, pacemakers, defibrillators, and cardiac resynchronization.
- Baseline Signs Monitoring: Focuses on monitoring basic physiological parameters such as blood glucose, blood pressure, temperature, and oxygen saturation. Compact trackers, smartwatches, and electric stethoscopes analyze and transmit the data to medical providers.
- Pregnancy Monitoring: Gathers information on a mother’s and fetus’s health to identify any irregularities, no matter how small.
- Depression Monitoring: Evaluates a person’s heart rate, blood pressure, level of physical activity, and sleep habits to identify mood swings and signs of depression.
Struggling With RPM Integration? Our Custom Solutions Simplify Deployment and Enhance Patient Care Efficiency
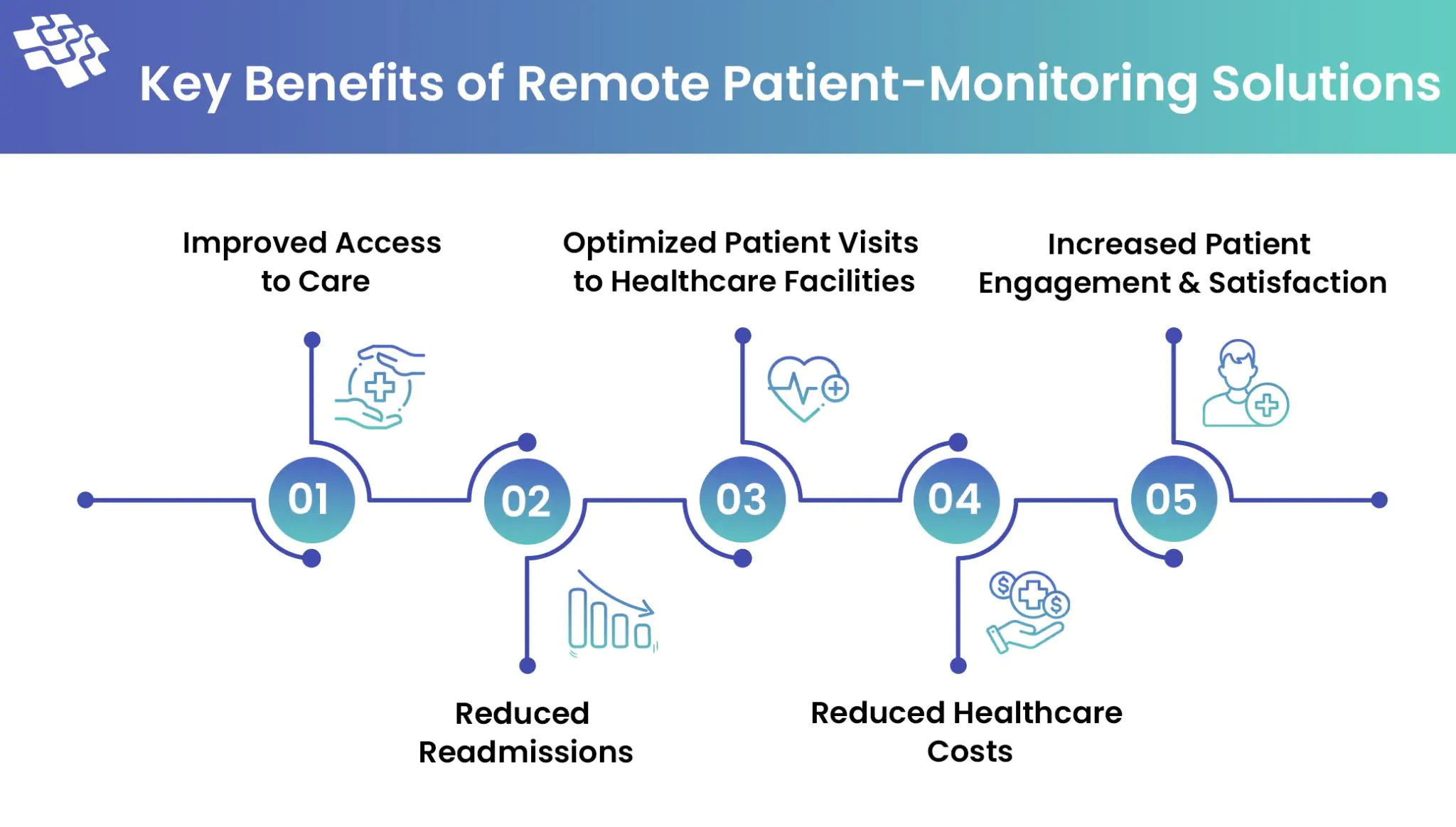
Key Benefits of Remote Patient Monitoring Solutions
Compared to 20% in 2021, more than 81% of practitioners utilized RPM on patients in 2023, a 305% increase. Numerous variables that are advantageous to patients and healthcare practitioners are driving the growing use of RPM instruments, which range from wearables to more complex devices like pulse oximeters and ECGs.
- Improved Access to Care: Remote patient monitoring services increase access to care by delivering it to patients at their location. Patients who live in remote places or have restricted mobility will benefit from this improved accessibility. 65% of physicians in both urban and rural locations use remote patient monitoring for medical treatment. For at-risk groups, remote patient monitoring applications are also a lifeline, enabling elderly or immunocompromised people to manage their medical conditions from the comfort of their own homes.
- Reduced Readmissions: Early identification keeps more beds available by preventing minor problems from developing into emergencies and hospitalizations. Early discharges are also made possible by remote monitoring technology, which enables physicians to closely observe recuperating patients from a distance. For instance, by giving patients pills and RPM equipment, the University of Pittsburgh Medical Center was able to minimize the incidence of hospital readmissions by 76%.
- Optimized Patient Visits to Healthcare Facilities: According to a recent poll, almost 70% of patients in the 40+ age range would be willing to use an RPM device if it allowed them to see doctors and hospitals less frequently. Furthermore, when it comes to cutting down on inpatient care hours for the following groups, remote patient monitoring solutions are indispensable: Individuals with chronic conditions, those with significant disabilities, elderly individuals requiring specialized care, post-surgery patients in need of rehabilitation. Medical personnel can monitor patients who fit into these categories by using telemedicine solutions and/or remote patient-monitoring kits, which will cut down on needless hospital stays and doctor visits.
- Reduced Healthcare Costs: In addition to saving lives, remote monitoring technology can also save money. Globally, RPM is predicted to save healthcare expenses by $200 billion over the next 25 years for all illnesses. Early interventions, lower hospital readmission rates, better chronic illness management, and less work for doctors are just a few of the ways that technology helps save money.
- Increased Patient Engagement & Satisfaction: 40% of those with chronic illnesses desire greater control over their health care. RPM tools can help by providing people with greater control over their health and putting important health information at their fingertips. RPM platforms increase drug adherence, encourage healthier lifestyle choices, and foster a stronger feeling of patient ownership over their health journey by making it easier for patients to engage in treatment.
- Alerts & Notifications: Important notifications for patients and doctors, like prescription reminders and appointments that may need to be attended to right away.
Want Real-Time Insights? Transform Care with Our Advanced RPM Solutions Powered by AI & IoT
Features to Include in Remote Patient Monitoring Solutions
It’s critical to differentiate between basic and advanced functionality when creating RPM software and to include customization and customization choices. This strategy ensures that the app can meet a wide range of requirements, from basic health monitoring to complex healthcare administration. To ensure basic health monitoring, medication management, and secure communication between patients and doctors, every remote monitoring software should include the following essential features:
- Symptom Logging: A straightforward and user-friendly method for patients to document their symptoms and any modifications to their health.
- Medication Management: Features for monitoring adherence and scheduling medication reminders help ensure that patients are regularly adhering to their recommended treatment regimens.
- Vital Signs Monitoring: The capacity to monitor vital health indicators like blood pressure, heart rate, blood sugar, and oxygen saturation.
- Appointment Management: The capability for patients to make, change, or cancel appointments with their medical professionals.
- Secure Messaging: A private and safe way for patients and medical professionals to communicate.
- Health Data Security: Utilizing encryption and adherence to US health data protection regulations, such as HIPAA, to ensure patient data confidentiality and privacy.
- Alerts & Notifications: Important notifications for patients and doctors, like prescription reminders and appointments that may need to be attended to right away.
How to Build Reliable RPM Software: Key Steps
Healthcare professionals must invest adequate time in obtaining firsthand knowledge of users’ requirements. An RPM system that ensures total patient satisfaction can only be constructed in this manner. The following steps must be followed to develop an effective RPM software system:
1. Requirements Gathering
The following phases make up the requirements-gathering stage:
- We must identify the stakeholders or those who will use and be influenced by the system, including administrators, patients, caregivers, and healthcare practitioners.
- Review current patient monitoring procedures, pinpoint development opportunities, and analyze the resources required in terms of the technological stack, system requirements, infrastructure setup, etc. as part of a needs assessment.
- The next step is to specify the non-functional criteria, including the system’s performance metrics in terms of accuracy and response time, as well as the functional requirements, like what the patient’s vital signs must be tracked.
- Prioritizing and validating the criteria through focus groups and patient surveys is necessary.
2. System Architecture Design
To comprehend the whole scope and influence of the final system design, the RPM system architecture design process necessitates constant communication with the pertinent stakeholders. The steps to put this into practice are as follows:
- Consult with patients, healthcare providers, and IT specialists serving as administrators to fully understand the scope and requirements of the system.
- Describe the sources of patient data, including sensors that use wearables and other devices to record vital signs, past medical information, diagnostic history, etc.
- Select the most practical communication method and a database that offers the highest level of security and privacy for your data.
- Create a user-friendly interface that both patients and doctors can rapidly become proficient with.
- Make sure the system architecture is scalable, test and validate it frequently, and keep an eye on it to strengthen its dependability and security.
3. Prototyping
Research is important, but you also need to test the hypotheses and solutions you develop. Even when assumptions are supported by facts, they might occasionally be quite different from what works. Developers typically produce a minimal viable product to test research findings. The primary features and suggested design are included in an MVP. You can make improvements to the suggested plan based on the feedback from the initial users. If you had to make the updates at the last minute, it would cost more and take much more work.
After developing a prototype, you ought to create a thorough schedule, a list of tasks, and a more precise budget.
4. Develop Software & Ensure Hardware Integration
Most of the software development lifecycle is devoted to the RPM system’s implementation or development phase. The following are some of the various sub-stages that comprise the development:
- Setting Up Modules: Every module in the remote patient monitoring system is independent and performs a distinct task. Together with making sure the code is scalable, expandable, and capable of reliable maintenance, these modules should be well-structured.
- Programming the RPM: Following the selection of the most practical technology stack in terms of databases, frameworks, and programming languages, the actual code-writing process begins. Write securely annotated, scalable lines of code that adhere to the most recent coding standards.
- UI Development: The goal of the system’s User Interface development should be to make it platform-agnostic and responsive.
- Database Development: The database should be created with the most important compliance criteria for the healthcare sector in mind. Additionally, to ensure the security of private patient information, HIPAA compliance needs to be monitored.
- Version Control: Since the development team adheres to standard practices for branching and merging the codebase, an effective version control system must be put in place to monitor code changes and ensure codebase consistency.
5. Test the App to Improve Quality
Testing is central for all apps. However, a bug in a video player, for instance, is forgivable. It will only influence the entertainment-related aspects of a user’s life. The situation is different for the healthcare sector. A bug in the RPM software can sometimes be fatal. For example, if the blood sugar monitoring app provides an incorrect result, there’s a risk of creating a false sense of security in a patient.
Users of one of the glucose monitors suffered serious injuries from malfunctioning audio systems. They may have to postpone an emergency room visit due to an inaccurate result, which could cause serious health problems or even death. Because of this, RPM frameworks necessitate hiring more testers than is customary. When developing healthcare software, you should budget more for security.
6. Update the App
Prototyping alone cannot identify every problem with a given RPM solution. Indeed, it is possible to predict the patients’ possible issues. However, our minds and biology are sufficiently intricate to produce some surprising results. This implies that work continues after a product is released. After getting comments, you need to update the program and hardware.
Without this, you run the danger of running into potentially fatal flaws (even the most rigorous testing may overlook certain behaviors) and deterring consumers from using your program because of its poor user experience. Development in the RPM industry doesn’t stop with a product’s introduction; to handle increasingly emerging issues, you must continuously work to make the product more patient-friendly.
Future Directions to Advance Remote Patient Monitoring Services
As healthcare systems develop, there are numerous opportunities for remote patient monitoring systems in the future. It is expected that RPM will develop in several important ways that will increase its potential and influence.
- Integration with AI and ML: More complex patient data analysis will be possible with RPM systems that include AI and ML algorithms and EHR integration. Early intervention and individualized treatment strategies are made possible by predictive analytics’ ability to foresee health patterns.
- Patient-Generated Health Data Utilization: RPM will place more emphasis on patient-generated health data in the future. This offers a comprehensive picture of a patient’s health by incorporating not just physiological data but also lifestyle information and patient-reported outcomes.
- Remote Diagnostic Capabilities: Remote testing for health markers can be made possible by diagnostic technologies included in future RPM systems. More complex diagnostic features built into wearable technology or at-home testing kits for chronic illnesses could be examples of this.
- Telehealth Synergy: A smooth patient experience will be achieved through additional integration with telehealth services. RPM and telehealth working together will allow for virtual consultations in addition to remote monitoring, delivering full-scope medical treatment right to patients’ homes.
Conclusion
Remote patient monitoring is no longer just an option—it’s an essential component of modern healthcare. Over the decades, RPM has evolved to deliver significant improvements in patient outcomes, operational efficiency, and cost savings, making it a cornerstone of value-based care. Public and private payers recognize its potential, leading to increased patient access and demand for RPM solutions. To meet this growing need, organizations must adopt innovative technologies and partner with experts in remote patient monitoring software development.
The future of remote patient monitoring services lies in continuous innovation and adoption. With advancements in AI, IoT, and custom AI mHealth app development, businesses can develop more efficient, scalable, and patient-centric solutions. However, success depends on selecting a reliable software partner who adheres to the highest standards and compliance frameworks, ensuring data security, seamless integration, and scalability.
If you’re ready to enhance your healthcare services with robust RPM solutions, contact us today to learn how we can help you succeed in this transformative journey.
Frequently Asked Questions About Data-driven Innovation in Clinical Pharma
Related Blogs
How is Predictive Analytics in Healthcare Revolutionizing It
Imagine if medical professionals could foresee your health problems before they become critical. Predictive analytics in healthcare is real and not just science fiction.
How AI in Clinical Trials is Improving Patient Outcomes
The past year has seen a lot of coverage of AI because of its potential applications in business, logistics, technology, healthcare, and other fields. What about clinical research, though?
The Role of AI in Personalized Healthcare
The World Economic Forum projects that by 2030, AI in personalized healthcare will be valued at $188 billion worldwide. Due to the increased healthcare needs of the aging population...
Stay In the Know
Get Latest updates and industry insights every month.